How many neurons in the human body? This question has intrigued scientists for centuries, as these intricate cells form the foundation of our thoughts, emotions, and actions. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of neurons, exploring their significance, distribution, and the factors that shape their numbers.
Neurons, the fundamental units of the nervous system, are specialized cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. They play a pivotal role in everything from movement and sensation to cognition and memory. Understanding the number of neurons in the human body is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of the brain and its impact on our overall health and well-being.
Introduction
Neurons are the fundamental units of the nervous system, responsible for transmitting information throughout the body. They are specialized cells that generate, transmit, and process electrical and chemical signals, enabling communication between different parts of the body and the brain.
Neurons play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including movement, sensation, thought, memory, and emotion. Their proper functioning is essential for overall health and well-being.
The Structure of a Neuron
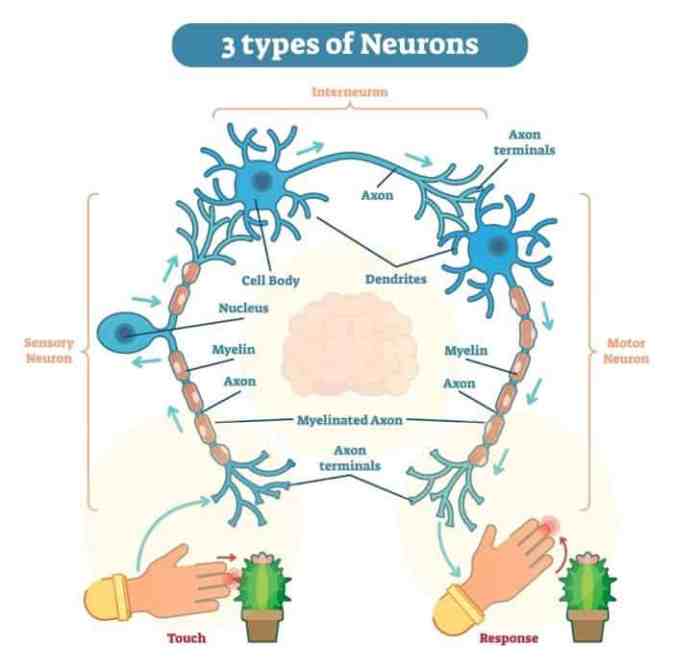
- Cell Body:The cell body, also known as the soma, contains the nucleus and other organelles essential for the neuron’s survival.
- Dendrites:Dendrites are branched extensions of the cell body that receive signals from other neurons.
- Axon:The axon is a long, slender projection that transmits signals away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles.
- Myelin Sheath:In some neurons, the axon is covered by a myelin sheath, which acts as an insulating layer, increasing the speed of signal transmission.
Methods for Estimating the Number of Neurons in the Human Body: How Many Neurons In The Human Body
Determining the precise number of neurons in the human body remains a challenging task due to the vastness and complexity of the nervous system. However, scientists have developed various techniques to provide estimates of this immense neuronal population.
Histological Analysis
Histological analysis involves examining thin tissue sections under a microscope to count neurons directly. This method is labor-intensive and prone to sampling errors, as it only provides a small snapshot of the entire brain or nervous system.
Stereological Methods
Stereological methods use statistical sampling techniques to estimate the number of neurons in a given volume of tissue. These techniques involve creating a series of parallel sections and counting the number of neurons within a known area or volume. The total number of neurons is then extrapolated based on the sampling data.
Computational Modeling
Computational modeling utilizes mathematical models and algorithms to simulate the structure and function of the nervous system. These models can be used to estimate the number of neurons based on various parameters, such as brain volume, neuronal density, and synaptic connectivity.
Distribution of Neurons in the Human Body
The human body is a complex network of neurons, which are the fundamental units of the nervous system. These neurons are distributed throughout the body, forming the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system.
Brain
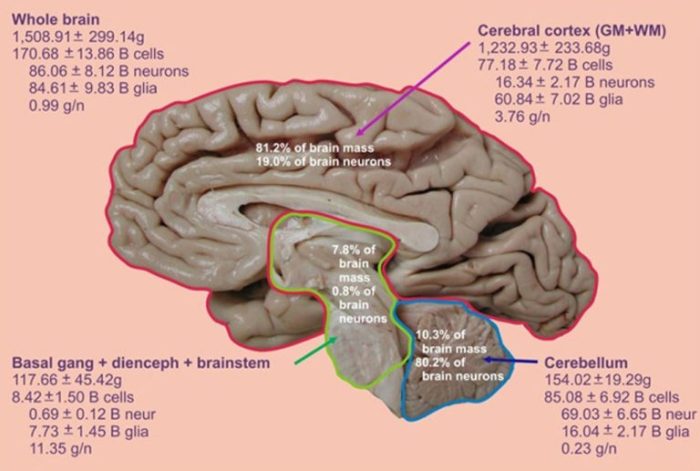
The brain is the central processing unit of the nervous system, containing an estimated 86 billion neurons. These neurons are organized into different regions, each responsible for specific functions such as movement, sensation, memory, and cognition.
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, cylindrical structure that extends from the brainstem to the lower back. It contains approximately 1 billion neurons, which transmit signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system consists of all the nerves that connect the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. It contains approximately 100 billion neurons, which are responsible for transmitting sensory and motor signals between the central nervous system and the body’s organs and tissues.
Factors Influencing the Number of Neurons
The number of neurons in the human body is not fixed and can be influenced by various factors. These factors include:
Age
As we age, the number of neurons in the brain decreases. This is a natural process that begins in adulthood and continues throughout life. The rate of neuron loss varies depending on the brain region, with some areas losing neurons more rapidly than others.
Gender
Studies have shown that men have a slightly higher number of neurons in the brain than women. This difference is thought to be due to the larger size of the male brain.
Environmental factors
Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as toxins and radiation, can damage neurons and lead to a decrease in their number. Additionally, factors such as stress, diet, and exercise can also affect neuron health and survival.
Clinical Implications of Neuron Count
The number of neurons in the human body has significant clinical implications, providing insights into the health and functioning of the nervous system. Understanding neuron count can aid in the diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment of various neurological conditions.
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, are characterized by the progressive loss of neurons. By measuring neuron count, researchers can track the progression of these diseases and assess the effectiveness of potential treatments.
Traumatic Brain Injuries, How many neurons in the human body
Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) can result in significant neuronal damage. Estimating neuron count can help determine the severity of the injury, predict outcomes, and guide rehabilitation strategies.
Developmental Disorders
Developmental disorders, such as autism and schizophrenia, have been linked to abnormalities in neuron count. By examining neuron count in individuals with these conditions, researchers can gain insights into their neurobiological underpinnings and develop targeted interventions.
Future Research Directions
Understanding the exact number of neurons in the human body remains a complex and challenging task. Future research should focus on refining existing methods and exploring new approaches to obtain more accurate and comprehensive estimates.
One promising area of research is the development of non-invasive imaging techniques that can visualize and quantify neurons in the living human brain. This could involve advancements in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), or other neuroimaging modalities.
Technical Advancements
- Exploring the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to analyze large datasets and identify patterns in neuron distribution.
- Developing computational models that simulate neuron growth and connectivity to predict neuron counts in different brain regions.
- Investigating the relationship between neuron count and cognitive function to better understand the impact of neuronal loss on brain health.
Epilogue
As we continue to unravel the intricacies of neuron count, future research holds the key to unlocking new insights into neurodegenerative diseases, traumatic brain injuries, and developmental disorders. By delving deeper into the world of neurons, we pave the way for advancements in human health and well-being, empowering us to harness the full potential of our extraordinary brains.
FAQ Summary
What are neurons?
Neurons are specialized cells that transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body, forming the foundation of the nervous system.
Why are neurons important?
Neurons play a crucial role in everything from movement and sensation to cognition and memory, shaping our thoughts, emotions, and actions.
How do scientists estimate the number of neurons in the human body?
Scientists use various techniques to estimate neuron count, including histological analysis, stereological methods, and computational modeling.
How many neurons are in the human brain?
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons, forming intricate networks that govern our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
Can the number of neurons in the human body change over time?
Yes, the number of neurons can change over time due to factors such as age, gender, and environmental influences.